Omega-3 vs Omega-6: Key Benefits for Your Heart and Health
Imagine you’re shopping in the grocery store, looking at different cooking oils. Some labels say “omega-3” or “omega-6,” and you wonder what they mean. Maybe your doctor has mentioned them before, but you’re not sure how they affect your health. Don’t worry, I’ll help you!
Omega-3 and omega-6 are types of healthy fats called essential fatty acids. That means your body needs them, but it can’t make them on its own; you have to get them from food. Omega-3 fats are great for your heart, brain, and joints. They help lower inflammation and keep your body working well. You can find them in foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Omega-6 fats are also important. They give you energy and help with growth and repair. They’re found in oils like sunflower, corn, and soybean oil. But here’s the thing: most people eat too much omega-6 and not enough omega-3. Getting the right balance is key for good heart health and less inflammation in the body.
So next time you see those labels, you’ll know what they mean and how to make a better choice for your health.
I’ll break down everything you need to know about omega-3 vs omega-6, their unique benefits, and how to optimize your intake for maximum health benefits.
What Are Omega Fatty Acids? Understanding the Basics
Think of omega fatty acids as healthy fats your body needs but can’t make by itself, kind of like how you need vitamins from food. These are called “essential fatty acids” because you must get them through your diet.
Omega-3 and omega-6 are part of a group called polyunsaturated fats. The numbers (3 and 6) tell scientists where a bond sits in its structure, but you don’t need to worry about that. What matters is how they affect your health.
Here’s how they are different:
Omega-3 fats help reduce swelling in the body. They support a healthy heart, help your brain work well, and can ease joint pain.
Omega-6 fats are helpful, too; they give your body energy and help with healing. But too much can cause too much swelling or inflammation, which isn’t good.
What matters most is balance. Your body needs both, but today’s diets often have too much omega-6 and not enough omega-3, which can lead to health issues.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Heart Protector
Omega-3 fatty acids are like having a personal bodyguard for your cardiovascular system. Let’s explore why these healthy fats deserve a starring role in your diet.
Types of Omega-3s You Should Know
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): Mostly found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, EPA helps fight inflammation. It lowers the swelling in your body, which can harm your blood vessels and lead to heart problems.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): Also found in fish, DHA is very important for your brain and eyes. Since about 60% of your brain is made of fat, DHA plays a big role in keeping your brain and vision healthy.
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): Found in plant foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, ALA is a type of omega-3 that your body can turn into EPA and DHA. But your body doesn’t do this very well, so it’s still best to eat fish or take supplements for EPA and DHA.
Heart Health Benefits That Matter
Studies have clearly shown that omega-3 fats are very good for your heart:
Lower Risk of Heart Disease: People who often eat fatty fish have a much lower chance of getting heart disease. Omega-3s help keep your heart beating normally and reduce the risk of serious rhythm problems.
Lower Blood Pressure: EPA and DHA can help relax the blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow. This helps lower blood pressure and reduces strain on the heart.
Better Cholesterol Levels: Omega-3s can raise your “good” HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides, which are fats in your blood that can increase the risk of heart disease if too high.
Less Inflammation: Long-term inflammation in the body can slowly damage your arteries. Omega-3s are natural anti-inflammatory agents that help calm this harmful process and protect your heart.
Beyond Heart Health: Other Omega-3 Benefits
Brain Function: DHA is very important for memory, focus, and overall brain health. Some studies show that getting enough omega-3s may help slow down memory loss and thinking problems as you get older.
Eye Health: The retina, which helps you see, has a lot of DHA in it. Eating enough omega-3s may help protect your eyes from problems like dry eyes and age-related vision loss, such as macular degeneration.
Mental Health: Research suggests omega-3s can support a healthy mood. They may help manage feelings of depression and anxiety by supporting brain chemistry and reducing stress in the body.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids: The Misunderstood Fat
Omega-6 fatty acids are often seen as the “bad fats,” but that’s not really fair. Just like omega-3s, omega-6 fats are essential, which means your body needs them to stay healthy. They help with brain function, support growth, and play a role in your body’s natural healing processes. The real issue isn’t with omega-6 itself it’s how much we eat.
In a healthy diet, there should be a balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fats. However, most people today eat far more omega-6 than omega-3, mostly because of processed foods and vegetable oils like corn, sunflower, and soybean oil. This imbalance can lead to inflammation, which is linked to heart disease, joint pain, and other health problems.
So, while omega-6 is not bad, getting too much without enough omega-3 can cause problems. The goal is to eat both but in the right ratio. Try to include more omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts in your meals, and limit processed foods high in omega-6. That way, your body gets the healthy fats it needs without the extra risk.
Types of Omega-6s in Your Diet
Linoleic Acid (LA): This is the most common type of omega-6 fat in most people’s diets. It’s found in foods like vegetable oils (such as sunflower, corn, and soybean oil), as well as in nuts and seeds. Your body can take LA and turn it into other useful omega-6 fats when needed. It plays a role in keeping your skin, cells, and overall health in good shape.
Arachidonic Acid (AA): This omega-6 fat is mostly found in animal products like meat, eggs, and dairy. AA is important for your immune system and helps your cells send signals to each other. However, having too much AA in your diet can lead to extra inflammation, which may cause health problems if not balanced with enough omega-3s.
The Real Benefits of Omega-6
Even though omega-6 fatty acids often get a bad name, they have many important health benefits:
Skin Health: Linoleic acid, a type of omega-6, helps protect your skin by keeping it soft and moist. It stops water from escaping and blocks harmful stuff from getting in. People with dry skin or eczema often have low levels of this fat.
Immune Support: Omega-6 fats help your immune system work properly. They play a role in inflammation, which your body uses to fight off infections and heal wounds.
Growth and Development: These fats are very important for healthy growth, especially in babies and children. They help with building and repairing body tissues.
Cell Health: Omega-6 fats are part of the outer layer of all your cells. They help keep cells strong and working the way they should.
Getting the right amount of omega-6 along with enough omega-3 is key to good health.
Why Omega-6 Gets a Bad Reputation
The problem with omega-6 fatty acids isn’t that they are bad for you. It’s that most people eat way too much of them compared to omega-3s. This imbalance can cause several health issues, such as:
More inflammation in the body
Higher risk of heart disease
Increased chances of autoimmune problems
Trouble using omega-3s properly in the body
Here’s an easy way to understand it: omega-6 fats act like the gas pedal for inflammation, while omega-3s work like the brakes. Your body needs both to stay in balance. But if you keep pressing the gas without using the brakes, things can go wrong. To stay healthy, it’s important to reduce excess omega-6s (often from processed foods) and eat more omega-3-rich foods like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. That way, your body gets the right balance it needs to function well.
The Critical Balance: Understanding the Omega-3 vs Omega-6 Ratio
This is where it gets really important and where many people make mistakes. The balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fats in your diet can have a big effect on your overall health.
What’s the Ideal Ratio?
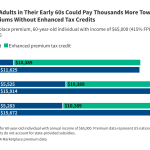
Experts say the best balance of omega-3 to omega-6 fats is between 1:1 and 1:4. That means for every gram of omega-3 you eat, you should have no more than 4 grams of omega-6.
Long ago, our ancestors probably ate close to a 1:1 ratio. But today’s modern diet—full of processed foods and vegetable oils—has changed that. Now, most people eat way too much omega-6, with a ratio around 1:10 to 1:25. This means they’re getting 10 to 25 times more omega-6 than omega-3, which can lead to health problems like inflammation, heart disease, and poor brain function.
Balancing this ratio by eating more omega-3-rich foods and cutting back on processed oils is key to better health.
How Modern Diets Went Wrong
How Modern Diets Went Wrong
Many things have caused this unhealthy balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fats:
More Vegetable Oils: Oils like corn, soybean, and sunflower are very high in omega-6. These are now used in most packaged foods and in cooking at restaurants.
Less Fish in the Diet: Fatty fish like salmon and sardines are rich in omega-3s, but many people don’t eat them often.
Factory-Farmed Animals: Animals raised on grains instead of grass make meat and dairy that have more omega-6 and less omega-3.
More Processed Foods: Most ready-to-eat snacks, baked goods, and fast foods are made with oils high in omega-6, adding to the imbalance.
All of these changes in the modern diet have pushed omega-6 levels way up while omega-3 intake has gone down. This shift can lead to more inflammation and long-term health issues.
What Happens When the Balance Is Off?
When the balance between omega-3 and omega-6 is way off, your body becomes more inflamed. This long-term inflammation can lead to:
A higher risk of heart disease
More chances of getting autoimmune diseases
Slower healing after exercise or injuries
Mood swings, memory problems, or trouble focusing
More allergic reactions and sensitivity
The good news? You don’t need a complete diet overhaul. Just a few simple changes, like eating more omega-3-rich foods and cutting back on processed oils, can help bring your body back into balance and reduce inflammation.
Food Sources: Where to Find Each Type
Knowing which foods have omega-3 and omega-6 fats is important for keeping a healthy balance in your diet.
Top Omega-3 Foods
Fatty Fish (rich in EPA and DHA): Salmon (wild-caught is best),Mackerel,Sardines,Anchovies,HerringTuna (eat in moderation due to mercury)
Plant-Based Omega-3s (ALA): Flaxseeds and flaxseed oil, Chia seeds, Walnuts, Hemp seeds, Algae oil (a vegan source of EPA and DHA)
Other Good Sources: Grass-fed beef and lamb, Pasture-raised eggs, Grass-fed milk, yogurt, and cheese
Adding these foods to your meals can help improve your omega-3 intake and bring your body into better balance.
Common Omega-6
High Omega-6 Oils (use in small amounts): Corn oil, Soybean oil, Sunflower oil, Safflower oil, Cottonseed oil
Nuts and Seeds (nutritious but rich in omega-6): Almonds, Cashews, Pecans, Sunflower seeds, Pumpkin seeds
Other Sources:Poultry (especially with the skin), Pork, Most processed and packaged foods (like chips, cookies, and fast food)
These foods aren’t bad, but eating too many of them, especially without enough omega-3s, can throw off your fatty acid balance and lead to inflammation.
Smart Swaps for Better Balance
You don’t need to cut out omega-6 foods completely. That would be hard and not necessary. Instead, try making smart choices to improve your fat balance:
Use olive oil, avocado oil, or coconut oil instead of oils like corn or soybean
Pick grass-fed meat when you can instead of grain-fed options
Snack on walnuts. Sometimes, they have more omega-3s than other nuts
Mix ground flaxseed into your smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal for a plant-based omega-3 boost
Eat fatty fish like salmon or sardines 2–3 times a week for a steady source of EPA and DHA
These small changes can go a long way in helping you get the right balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, supporting better heart, brain, and overall health.
When You Might Need More of Each
You may need more omega-3s if you:
Don’t eat fish often
Have risk factors for heart disease (like high blood pressure or cholesterol)
Deal with ongoing joint pain or inflammation
Struggle with mood problems, anxiety, or depression
Have dry eyes or flaky, dry skin
You may need to focus on omega-6 balance if you:
Have very dry, rough, or damaged skin
Are a child or teenager going through a growth spurt
Have an autoimmune condition (like eczema or arthritis)
Are you healing from an illness, surgery, or injury
Paying attention to your symptoms and adjusting your omega-3 and omega-6 intake can support better health and help your body function at its best.
Conclusion: Your Action Plan-Simple Steps to Better Heart Health
Now that you know the importance of balancing omega-3 and omega-6 fats, here’s a simple plan to help you get started:
This Week:
Buy canned salmon or sardines and try them in a salad or sandwich
Use olive oil or avocado oil instead of vegetable oils for cooking
Add one tablespoon of ground flaxseed to your breakfast smoothies, oatmeal, or yogurt
This Month:
Try to eat fatty fish (like salmon or mackerel) twice a week
Snack on walnuts instead of other nuts
Check food labels and avoid items that list high omega-6 oils (like soybean or corn oil) near the top of the ingredients
Long-Term Goals:
Make fatty fish a regular part of your meals
Choose grass-fed meat when it fits your budget
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
Take an omega-3 supplement if you can’t get enough from food
Remember: Small changes over time can lead to big health improvements. You don’t need to change everything at once; just make better choices, one meal at a time.
Balancing your omega-3 and omega-6 intake is a powerful step toward protecting your heart and improving your overall health. Your body will thank you!
The post Omega-3 vs Omega-6 appeared first on Medifyhome.